
Providing Heat Recovery In Dust Collection Systems
Project designers and process owners often focus on filtering devices when designing or purchasing a dust collection system. Yet another area they focus on is
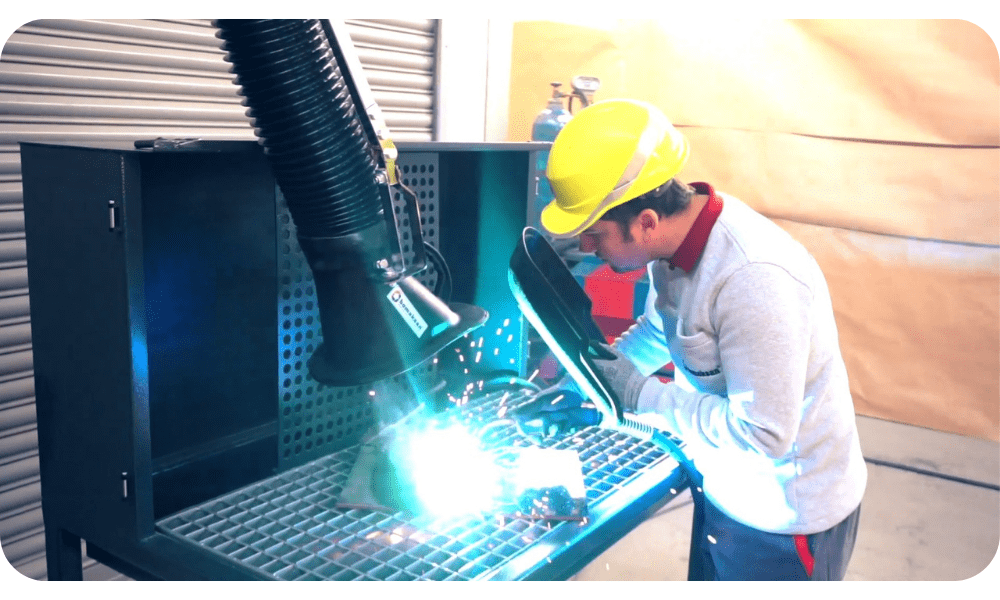

Extraction arms are the name given to suction apparatus that can move and allow operators to work flexibly. It usually consists of a suction hood, flex hose, spring or hydraulic piston support system, and wall, table or filter connection apparatus. It provides the capture and removal of pollutants released in a certain diameter according to the length of the extraction arm without spreading. So why are extraction arms so preferred?
ANSWER: GETTING CLOSER TO THE SOURCE OF POLLUTION
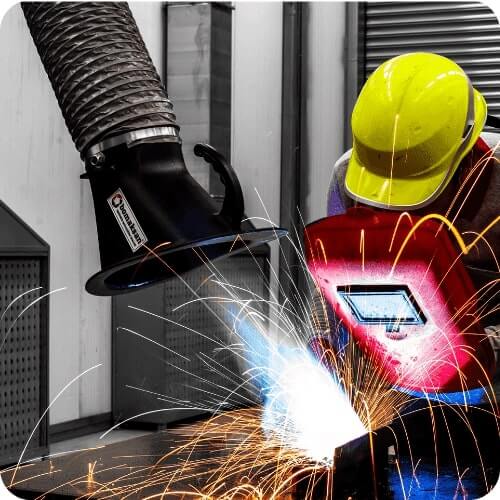

The most important reason why extraction arms are widely used and preferred in the industry is that they can get as close to the pollution source as possible. Approaching the pollution source means that the flow rate (needed to remove the dust, fume, and oil mist formed as a result of the production process) decreases. This naturally means a more compact filter unit and lower energy consumption. In other words, a system with a much more affordable initial investment and operating cost are possible with extraction arms. Different formulas are used according to the hood type when calculating the airflow needed to remove contaminants such as dust, fume, and oil mist.
The common feature of these formulas is that with the increase of the distance between the suction hood and the source of pollution, the required airflow increases (it increases by the square rate. In other words, if the distance is 2 times, the airflow requirement increases by 4 times.) Fixed hoods can approach a certain distance due to the production operation. Otherwise, they affect the working ergonomics and working performance of the operator. However, thanks to the easily movable extraction arms, the position of the extraction arm can be changed in accordance with the changing operation movements.
It is very important for extraction equipment to be positioned between the pollution source and the operator. Otherwise, the installed system will not protect the operator and the operator must take additional protective measures. In such systems where extraction hood cannot be positioned between the pollution source and the operator, the purpose of the dust collection and fume extraction system is to prevent the spread of pollution to other parts of the working environment and to protect other workers.
DISADVANTAGES OF EXTRACTION ARMS
The most important disadvantage of extraction arms is that they create higher resistance than fixed hoods. In other words, the suction fan should be designed in such a way that it can overcome a higher pressure in systems using extraction arms. Otherwise, the desired airflow rate will not be obtained.
Due to the nature of flexible hoses, fixed hoods are the first choice of system designers. Extraction arms are not preferred in systems that can be solved with fixed hoods. However, since this situation is very rare in real life, we encounter extraction arms in most of the processes.
WHEN EXTRACTION ARMS ARE NOT PREFERRED?
As mentioned above, extraction arms are not preferred if a suitable solution can be created with fixed hoods. The most important problem of fixed hoods is not getting close enough to the pollution source. For this reason, they have a much larger cross-sectional area to capture dispersed dust and fume. This increases the required airflow rate and creates the need for a larger dust collection system with higher energy consumption. However, fixed hoods can be positioned close to the source of pollution and if the cross-sectional area is relatively narrow, they are preferred over extraction arms.
Apart from this, there may be situations where the positions of the extraction arms need to be changed frequently. For example, in processes where large parts are welded, the welding position generally changes continuously and rapidly. In this case, the operator does not bother to constantly adjust the position of the extraction arm. In cases where neither fixed hoods nor movable hoods such as extraction arms are the solutions, the technique called general hall ventilation comes into play. The main purpose of General Hall Ventilation is not to protect the operator, but to protect other workers breathing the same air as the welding operator. For this reason, the welding operator should be equipped with additional safety equipment. (Like ventilated masks).
Case Studies

Project designers and process owners often focus on filtering devices when designing or purchasing a dust collection system. Yet another area they focus on is
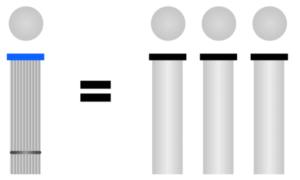
Whether it is industrial production or not, there are moments in every sector where the planned activities do not take place within the desired time

The most popular method of welding today is mild steel welding, which is important for every industry that uses welding in its production process. Latest
© 2017 - 2022 Bomaksan Industrial Air Filtration Systems. All Rights Reserved.